CCORE: CONNECTING SPACE AND ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES WITH SOCIETY AND THE FUTURE OF EXPLORATION.
MISSION:
CCORE is dedicated to advancing knowledge of Earth’s upper atmosphere and near-space environment through cutting-edge observation, research, and innovation. By fostering collaboration, developing technology, and training the next generation of scientists, CCORE strengthens both regional and global capacity for space science, exploration, and security.
VISION:
CCORE strives to be a leading hub at the forefront of Earth’s atmospheric and near-space research, driving global understanding of this critical environment, empowering future generations of scientists and innovators, and contributing to national security and space exploration.
Observations at CCORE generate data that advance forecasting, enhance safety in spaceflight, and bring scientific discoveries closer to everyday life.
ABOUT:
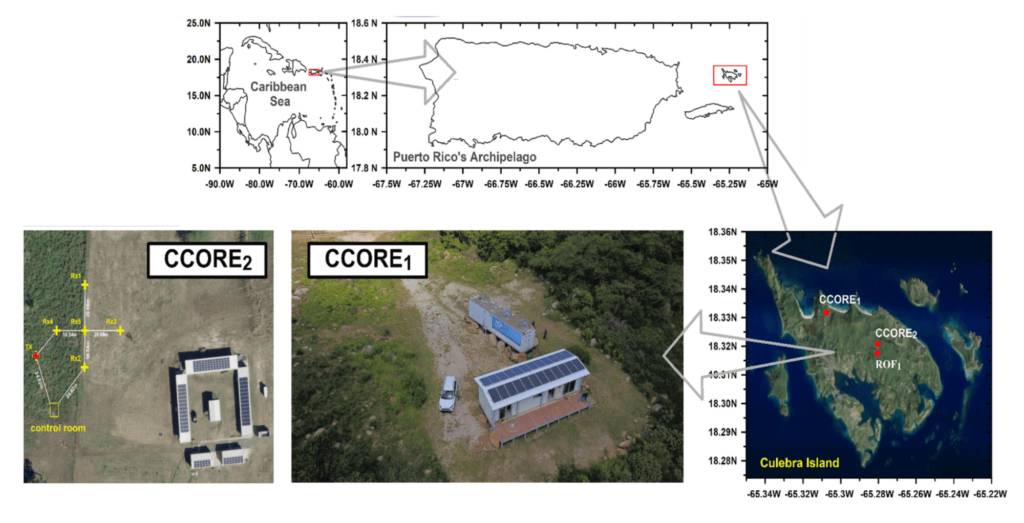
CCORE is located on Culebra, a small, preserved island northeast of the Puerto Rican archipelago. The island’s low population density and geographical features contribute to clear skies year-round, minimal light pollution, and very low radio frequency interference (RFI), making it ideal for optical and radio observations.
CCORE is the only geoscience facility in the U.S. Caribbean. It is strategically vital for space and atmospheric studies due to the configuration of geomagnetic field lines and the highly dynamic environment associated with convective forces in this region.
Founded in November 2015 as the Remote Optical Facility (ROF) of the Arecibo Observatory, it became CCORE following the Observatory’s closure in August 2023. CCORE is managed and supported by the Florida Space Institute at the University of Central Florida.
CCORE not only honors Arecibo’s remarkable legacy in space and atmospheric sciences but also actively enhances it by hosting and operating passive and radio instrumentation relocated from the original facility. Collaborating with various U.S. institutions, CCORE has become a vital player in national space-observational resources. Besides, CCORE stands as a dynamic platform for training, collaboration, and innovation.
The extensive database generated by CCORE has supported scientific proposals and peer-reviewed publications, been used to refine models, and deepened our understanding of Earth’s atmosphere and its transition to space. As an emerging research hub, CCORE signifies a transformative shift from a singular facility to an open research model, fostering robust collaborations in national space science and atmospheric sciences.

INFRASTRUCTURE AND OPERATIONS
The CCORE encompasses two units. CCORE unit 1 hosts four climate-controlled containers with optical and radio instruments, a control room, a weather station, and lodging for scientists and technicians. This unit is sustainable: a backup solar system feeds the facility, and rainwater is kept in a reservoir. This feature is particularly crucial for maintaining operations during the Atlantic Hurricane Season. CCORE unit 2 hosts a VHF all-sky Meteor Radar and a storage container.
The CCORE units smartly operate remotely 24/7. They have innovative features to monitor and control temperature, power outages, humidity, and other features required by each instrument. External and internal security cameras with motion sensors are installed in the outdoor areas and inside the containers to monitor the conditions of the units and instruments. Two local dedicated technicians support the operations and campaigns and troubleshoot the cluster of instruments.
CCORE’s current observational capability ranges from ~20 km to ~ 250 km of altitude and includes all-sky imagers, photometers, spectrometers, VLF receivers, HF receivers, red line Fabry-Perot interferometer, GNSSs, LF magnetic field sensors, radiometer, aerosol lidar, and VHF all-sky meteor radar.




CCORE’s Observational Capability
EDUCATION AND TRAINING:
CCORE is committed to offering the community and students opportunities to participate in scientific, engineering, and training activities related to space and atmospheric sciences. Through these initiatives, we aim to inspire and empower future generations. The activities at CCORE also seek to address the impacts of the Arecibo Observatory’s closure in Puerto Rico and to reduce the underrepresentation of Latin Americans in space sciences.
As an open research facility, CCORE aims to promote inclusivity and transparency through open access to data, platforms, tools, and services, allowing the community and students to participate actively in scientific, engineering, and training opportunities in space-and-atmospheric-related sciences.

CCORE TEAM
COLLABORATE WITH US:
CCORE is part of FSI, a non-profit soft money institution that relies on external funding. CCORE welcomes new collaborations through proposals and projects.



